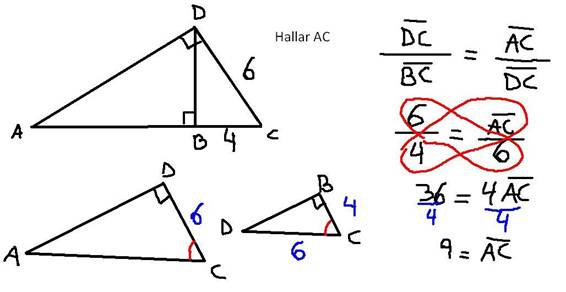
Este problema suele presentar algunas confusiones, muchas veces en el apuro o dados los nervios…
Proof Tables
A la hora de realizar las tablas , encontraremos infinidad de teoremas y conceptos que podemos utilizar, afortunadamente muchos de estos se repiten frecuentemente. Enumeraré las herramientas mas utilizadas junto con algunos ejemplos de cómo utilizarlas. Una vez adquirida la mecánica la resolución de las tablas suele ser bastante “lógica”.
Propiedades Lógicas
Transitive Property
If a=b and b=c , then a=c
Reflexive property
a=a
Symmetric Property
a=b then b=a
Similitud de triángulos
AA , SAS , SSS
Operaciones en la igualdad
Al operar de igual manera en ambos lados de una igualdad utilizaremos:
Subtraction property of equality
Addtition property of equality
Division property of equality
Multiplication property of equality
Congruencia de Triángulos
SSS , SAS , ASA , AAS
Para triangulos rectangulos:
HL
Una vez utilizados estos criterios puede utilizarse CPCTC: Corresponding Parts of Congruent Triangles are Congruent
Ángulos
Supplementary angles add up 180º
Complementary angles add up 90º
Alternate Interior anglesbetween parallels are congruent.
Alternate Exterior anglesbetween parallels are congruent.
Corresponding Anglesbetween parallels are congruent.
Consecutive Interior anglesadd up 180º
Consecutive Exterior anglesadd up 180º
Segmentos

AB+BC = AC Segment addition property
Siendo B punto medio de AC

AB=BC Definition of Midpoint
Ejemplo Proof Tables
Dado ABCD paralelogramo , probar que que los angulos ABC y ADC son congruentes